What is Body Dysmorphia?
Body dysmorphia is a mental health condition where individuals have a distorted perception of their appearance, often fixating on perceived flaws. It can cause severe distress and impact daily functioning. Individuals with body dysmorphia may obsess over their appearance and body image, leading to distress and impaired functioning.
What Causes Body Dysmorphia?
Body Dysmorphia can be caused by a combination of genetic, biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
Genetic Factors
A family history of mental health disorders can increase the risk of developing body dysmorphia.
Biological Factors
Chemical imbalances in the brain can contribute to the development of body dysmorphia.
Psychological Factors
Low self-esteem, distorted body image perceptions, negative self-evaluations, and cognitive biases can lead to an excessive focus on perceived flaws or imperfections.
Environmental Factors
Societal pressure, exposure to trauma or abuse, social and cultural pressures to conform to unrealistic beauty standards, and experiences of body shaming or bullying can all contribute to the development of body dysmorphia.
Hormonal Imbalances
Fluctuations in hormone levels can impact mood, self-perception, and body image, potentially contributing to body dysmorphia.
Disordered Eating Patterns and Chronic Dieting
A preoccupation with controlling body weight, shape, or size, often driven by societal ideals and media influence, can be associated with body dysmorphia.
What are the Symptoms of Body Dysmorphia?
Excessive Mirror Checking
Individuals with BDD may spend a significant amount of time checking their appearance in the mirror, often focusing on their perceived flaws.
Lack of Satisfaction with Physical Appearance
Avoidance Of Social Situations
Due to their preoccupation with their appearance, individuals with BDD may avoid social situations to prevent others from seeing their perceived flaws.
Constant Seeking Of Reassurance
Individuals with BDD may constantly seek reassurance from others about their appearance, but these reassurances often provide only temporary relief.
Excessive Grooming or Seeking Cosmetic Procedures
Individuals with BDD may engage in excessive grooming behaviors or seek multiple cosmetic procedures in an attempt to “fix” their perceived flaws.
Significant Distress or Impairment in Daily Functioning
The preoccupation with perceived flaws can cause significant distress and can interfere with the individual’s daily functioning, including their ability to work or maintain relationships.
Avoidance of Physical Activities and Strict Diets
Some individuals may avoid physical activities or adhere to strict diets in an attempt to change their perceived flaws.
Extreme Focus on Calorie Counting and Restrictive Eating Patterns
Individuals with BDD may exhibit an extreme focus on calorie counting and restrictive eating patterns, often driven by a desire to achieve a specific body shape or weight.
Feelings of Unworthiness, Anxiety, and Depression
Individuals with BDD often experience feelings of unworthiness, anxiety, and depression related to their appearance and perceived flaws.
Difficulty Maintaining Relationships and Social Isolation
The preoccupation with perceived flaws can lead to difficulties in maintaining relationships and can result in social isolation.
body dysmorphia treatments
What are the Treatments for Body Dysmorphia?
The best treatment for Body Dysmorphia is a combination of psychotherapy, medication, self-help strategies, support groups, and in severe cases, hospitalization or intensive outpatient programs.
Psychotherapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is often used to help individuals with body dysmorphia address distorted thinking patterns and develop healthy coping strategies.
Medication
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can alleviate symptoms of anxiety or depression that often accompany body dysmorphia.
Self-Help Strategies
Practicing self-compassion and challenging negative self-perceptions can be effective when used in conjunction with professional treatment.
Support Groups
These provide a sense of community and understanding, which can be very beneficial for individuals dealing with body dysmorphia.
Inpatient Treatment For Body Dysmorphia in Florida
Inpatient treatment for body dysmorphia involves a structured daily routine with individual and group therapy sessions. The focus is on promoting self-acceptance, challenging negative beliefs, and teaching coping skills.
Individual and Group Therapy
These sessions are designed to address the underlying thoughts and emotions contributing to the disorder. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure therapy are commonly used to challenge negative beliefs and decrease avoidance behaviors.
Medication Management
A comprehensive psychiatric evaluation is conducted to assess medication needs. Medication may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms of depression or anxiety, which often co-occur with body dysmorphia. Close monitoring and adjustments to medication are essential parts of the treatment process.
Family Therapy
This may be included to enhance understanding and support from family members. It helps the family to better understand the condition and how they can provide support.
Support Groups
Participation in support groups allows individuals to share their experiences, struggles, and successes with others who understand. Group therapy provides a supportive environment to discuss challenges related to body image, learn from peers, and gain valuable insights from different perspectives.
Recovery Coaching
This involves learning and practicing healthy coping skills, self-care, and creating a relapse prevention plan. The focus is on developing a sustainable recovery mindset beyond the treatment period, building a support network, and engaging in activities that promote self-esteem and body positivity.
Inpatient treatment is a comprehensive approach that addresses the multifaceted nature of body dysmorphia. It’s designed to provide the necessary tools and support to help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.

Treatment For Body Dysmorphia
Body Dysmorphia can be an isolating and overwhelming experience, but you don’t have to face it alone. At Still Mind Mental Health, we understand the intricate challenges of Body Dysmorphia. Our compassionate team is dedicated to providing you with personalized care, evidence-based therapies, and a supportive environment to help you navigate your journey to self-acceptance and well-being.
How to Help Someone with Body Dysmorphia?
Helping someone with Body Dysmorphia involves a combination of professional support, personal encouragement, and promoting a healthy lifestyle.
Encourage Professional Help
Encourage the individual to seek professional help such as therapy or counseling. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly effective for body dysmorphia.
Be a Supportive Friend
Be a listening ear and empathetic friend. Avoid making critical comments about their appearance or body, which can exacerbate their condition.
Promote a Healthy Lifestyle
Encourage a balanced lifestyle with nutritious eating habits and regular physical activity. This can help improve mood and boost self-esteem.
Advocate for Body Positivity
Advocate for acceptance and self-love for all body types. Encourage the individual to embrace their unique qualities and challenge societal beauty standards.
Suggest Self-Care Activities
Recommend activities such as practicing mindfulness, journaling, or seeking online resources. These can help improve self-image and build resilience against the negative effects of body dysmorphia.
Be Patient and Understanding
Recognize that body dysmorphia is a serious mental health condition that requires time and professional treatment to manage effectively.
Avoid Body Shaming Language
Focus on non-physical attributes when complimenting them. This can help shift the focus away from appearance and towards qualities that are not appearance-based.
Encourage Support Groups
Suggest joining support groups where they can share their experiences and learn from others who are going through similar experiences.
Does Social Media Trigger Body Dysmorphia?
Yes, social media can trigger body dysmorphia by promoting an unrealistic standard of beauty and promoting comparison.
However, it is important to remember that multiple factors contribute to this condition and more research is needed to fully understand the correlation.
To address this issue, it is crucial to:
Limit exposure to potentially triggering content
Practice self-compassion and mindfulness
Seek support if needed, such as therapy or counseling
Promote body positivity and authenticity, both personally and within your social media community
Teach and learn critical media literacy skills to challenge societal beauty standards and decipher idealized images
Remember, everyone’s experience with social media is unique, and it’s important to cultivate a healthy relationship with these platforms. If social media is causing distress, consider seeking professional help.
body dysmorphia vs dysphoria
Body dysmorphia and dysphoria are both psychological conditions, but they differ in their focus and manifestations.
Body Dysmorphia
This is a mental disorder characterized by obsessive thoughts and behaviors related to perceived physical flaws, causing significant distress. Individuals with body dysmorphia are preoccupied with one or more perceived defects or flaws in their physical appearance, which are not observable or appear slight to others. This preoccupation can lead to repetitive behaviors or mental acts in response to the appearance concerns.
Dysphoria
On the other hand, dysphoria is a general feeling of unease or dissatisfaction that can encompass many aspects of life, not just appearance. It is a state of discomfort or distress, and can be associated with depression, anxiety, or conditions like gender dysphoria, where a person experiences discomfort or distress because there’s a mismatch between their biological sex and gender identity.
While body dysmorphia focuses specifically on appearance-related concerns, dysphoria is a broader term that can be related to various factors. It is important to seek professional help if you or someone you know is struggling with either condition in order to effectively address and manage these challenges.
reverse body dysmorphia
How to Deal with Body Dysmorphia?
Dealing with body dysmorphia involves a combination of professional support, personal strategies, and lifestyle changes. Here are some ways to deal with body dysmorphia
Seek Therapy
Therapy can help explore and address the underlying causes of body dysmorphia, such as low self-esteem or trauma. A therapist can help develop coping strategies and challenge negative thoughts.
Adopt a Balanced Diet
Focus on adopting a balanced and nourishing diet, rather than obsessing over appearance. A nutritionist can guide you in making informed food choices that support overall health and well-being.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity that you enjoy, emphasizing strength and endurance over aesthetics, can enhance body confidence, improve mood, and promote self-care.
Join a Support Group
Connecting with others who have experienced similar struggles through a support group can provide validation, reduce feelings of isolation, and foster self-acceptance.
Practice Self-Compassion
Treat yourself with kindness and understanding. Focus on nurturing your emotional well-being and practicing self-care activities that bring you joy and fulfillment.
Remember, everyone’s journey with body image is unique, and progress takes time and patience. It’s important to seek professional help if you’re struggling with body dysmorphia.
Discover Inner Peace and Tranquility with Still Mind
Individual Treatment
Individual treatment at Still Mind offers personalized and focused therapy for individuals seeking support for their mental health challenges. It provides one-on-one sessions that address specific concerns, explore underlying issues, and develop tailored strategies for growth and healing.

Inpatient Treatment
Our luxury treatment center located in Fort Lauderdale, FL, we provide an environment free from distractions, allowing our residents to fully concentrate on their recovery and rest. Our team is committed to providing individualized treatment to each resident.

Dual Diagnosis
At our treatment center, we adopt an integrated approach to address dual diagnosis, finding key elements to helping ensure that substance use disorders and mental health disorders are treated effectively and simultaneously.
Trauma Treatment
With a deep understanding of the complex nature of trauma, the program provides a safe and nurturing environment for individuals to explore their trauma, process their emotions, and develop effective coping mechanisms.

Group Therapy
Group therapy involves multiple individuals with similar concerns who come together in a therapeutic setting facilitated by a trained therapist. It offers to share experiences, gain support from others facing similar challenge and develop social connections.

Residential Treatment
Residential treatment at Still Mind employs a comprehensive approach to care that has proven to be extremely successful in supporting patients in their journey toward long-term recovery and enhancing their overall well-being.
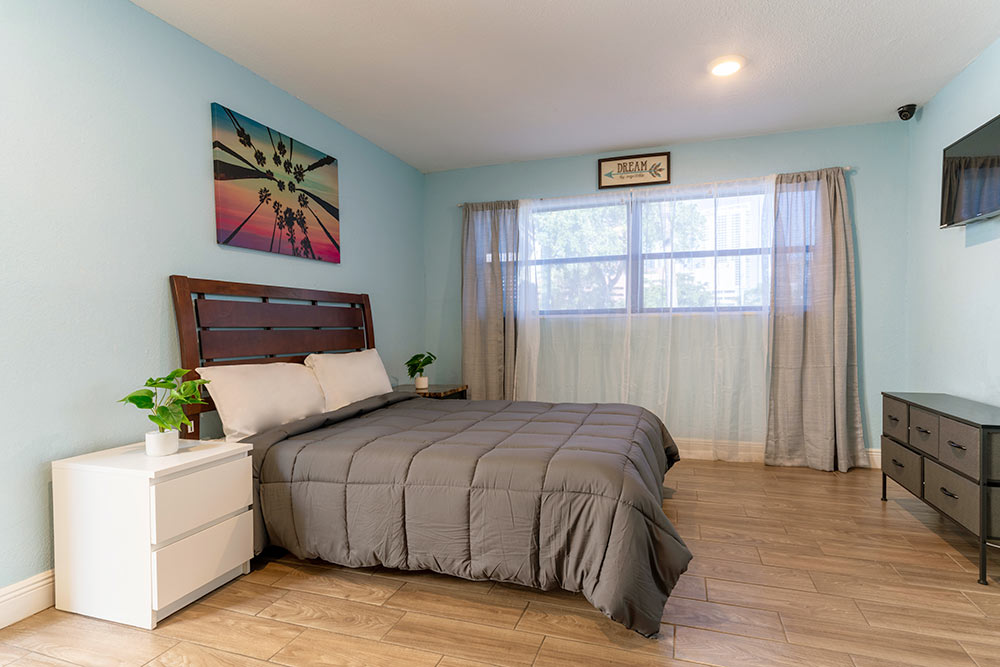
Accomodations
- Private Rooms
- Luxurious Beds
- Elegant Decor
- Ample Space for Personal Belongings
Amenities
- Tranquil Areas For Meditation
- Recreational Activities
- Culinary Experience & Personalised Meals
Facility
- Luxurious Residential Center
- 3,000 to 5,500 sq/ft Residence
- Expert Case Managers
- Masters Level Clinical Staff
Service Animals Are Welcomed
At our rehabilitation center, we believe that recovery should never come at the cost of leaving behind your service animal or altering your lifestyle. That’s why, unlike most facilities, we welcome service animals with open arms!
We understand the important role that these animals play in your life, and we’re committed to accommodating them throughout your journey with us.

Integrated Hollistic Approach
- Music Therapy
- Art Therapy
- Neurotherapy
- Psychodrama Therapy
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Life Skill Training

